Decentralized sequencers are rewriting the security playbook for rollups in 2025. As institutional adoption accelerates and use cases like tokenized assets and cross-border payments demand greater resilience, the era of centralized sequencing is being left behind. The risk calculus has shifted: single points of failure, censorship, and MEV extraction are no longer tolerable bottlenecks for scalable blockchain infrastructure.
Centralization’s Breaking Point: Why Sequencer Design Matters
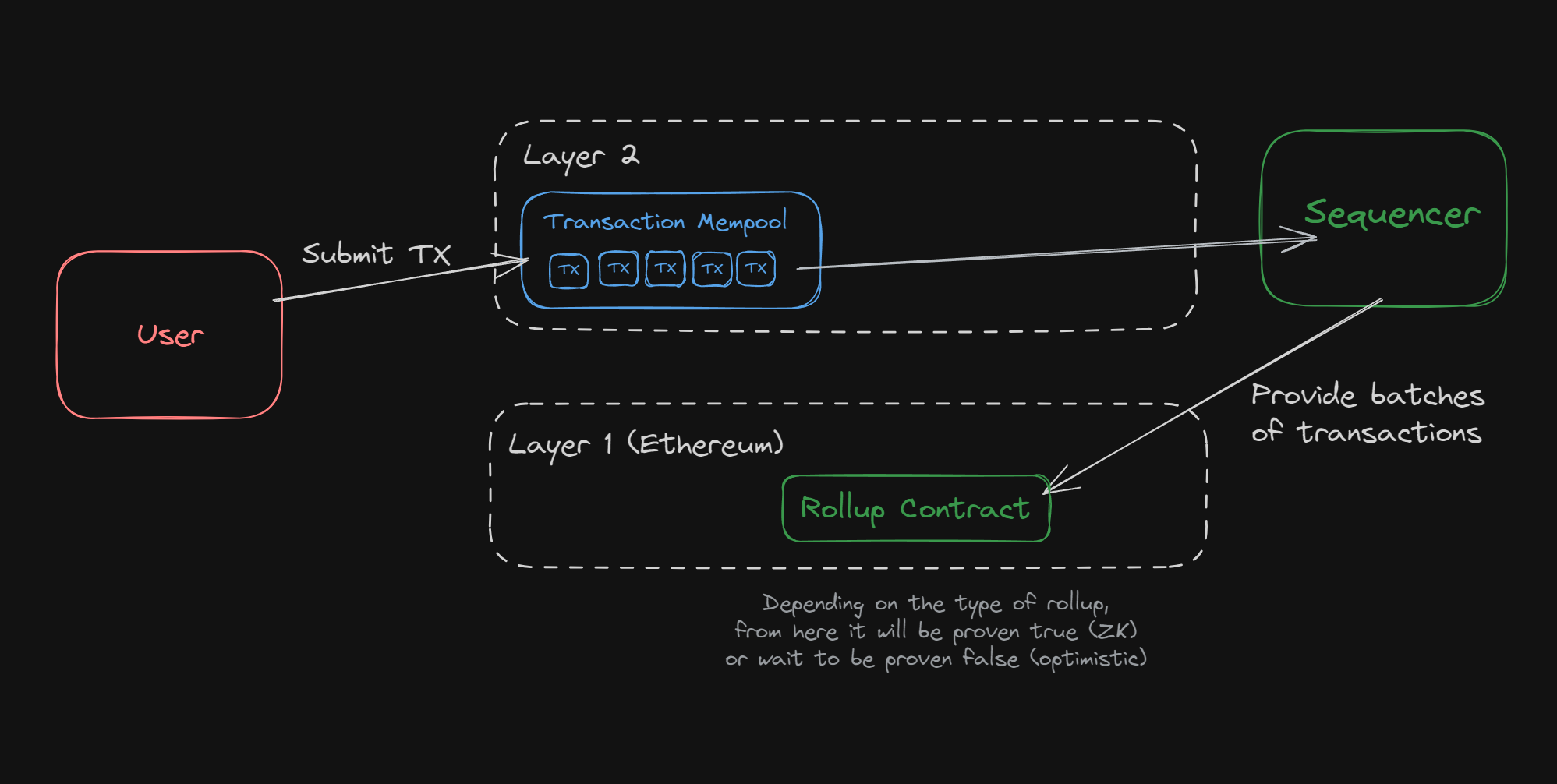
For years, rollup protocols relied on a single sequencer to batch transactions before posting them on-chain. This approach delivered speed and simplicity but at a steep cost. Centralized sequencers could censor transactions or reorder them for profit, undermining the very trustlessness that blockchains promise. In high-value environments – think DeFi protocols handling hundreds of millions – these vulnerabilities became glaring.
By late 2024, research and real-world exploits had made it clear: censorship-resistant rollups with fair transaction ordering aren’t optional; they’re essential for sustainable growth. Projects like Cero and Astria began rolling out hybrid and shared sequencer models, distributing control among permissioned or public node sets. The result? Increased liveness, stronger guarantees against downtime, and a measurable reduction in MEV-driven manipulation.
How Decentralized Rollup Sequencers Enhance Security
The technical leap is significant. In decentralized architectures, transaction ordering is handled by a committee or dynamically rotating set of nodes. These nodes use consensus algorithms – often leveraging Ethereum’s robust Proof-of-Stake layer or novel distributed sequencing strategies – to agree on transaction batches before finalizing them on L1.
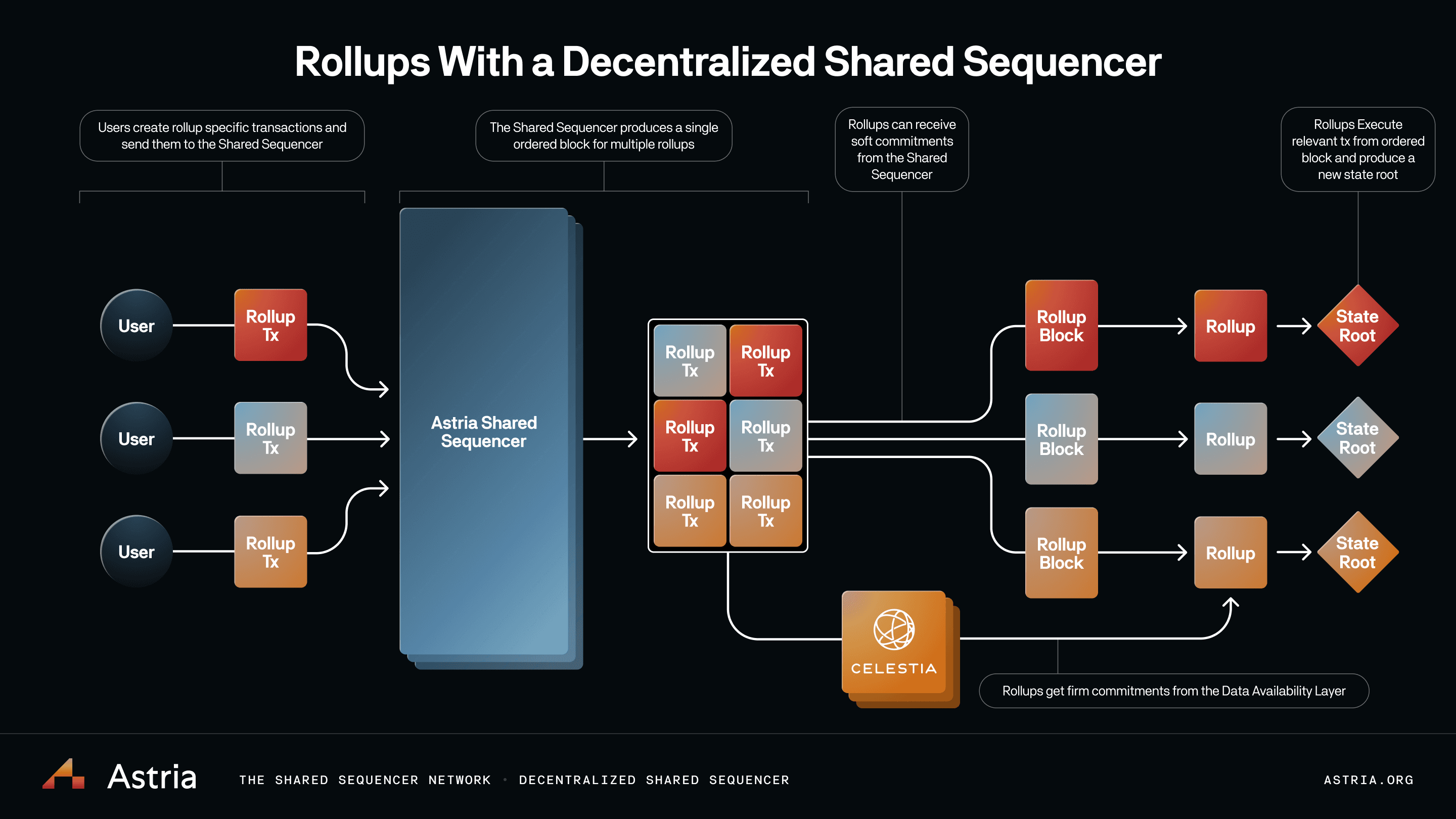
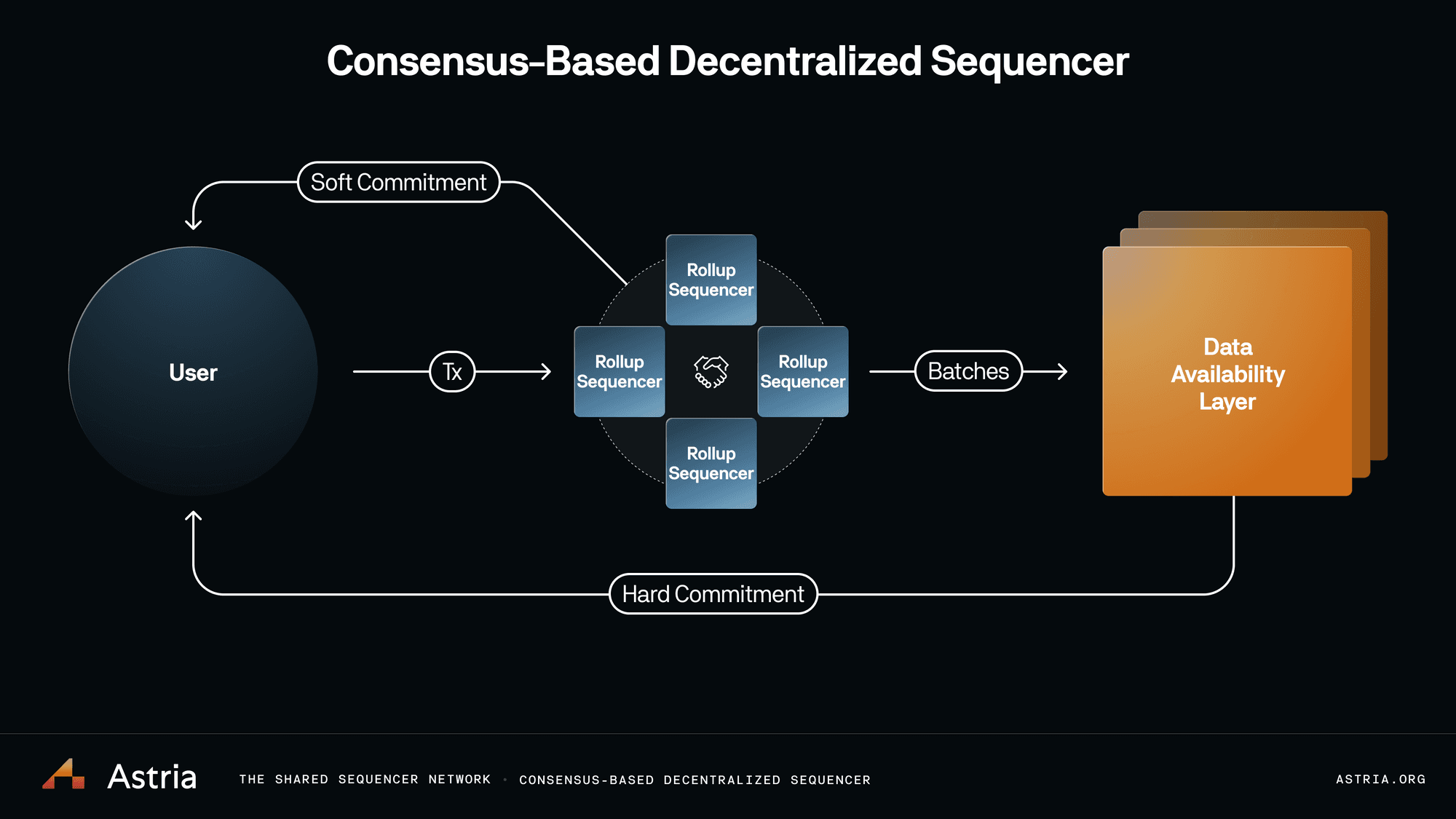
This structure eliminates single points of failure and makes censorship attacks costly or infeasible. For example, Cero’s hybrid model supports both permissioned and open participation, giving app-chain builders flexibility without sacrificing security attributes. Astria’s shared sequencer network processes blocks for multiple rollups at once, compressing data to lower costs while providing fast finality across chains.
- Resilience: Multiple nodes ensure no single actor can halt progress or censor users
- Censorship resistance: Transaction inclusion becomes probabilistic rather than discretionary
- MEV mitigation: Distributed sequencing removes unilateral power to reorder transactions for profit
This shift is already attracting major ecosystem players who recognize that decentralized rollup sequencers are foundational to next-gen blockchain scalability.
The Rise of Shared Sequencers and Based Rollups
A parallel trend is the emergence of shared sequencer networks. Instead of each rollup maintaining its own set of sequencers (fragmenting security), multiple chains now share a common sequencing layer. This model not only amplifies censorship resistance but also enables atomic cross-rollup trades and interoperability breakthroughs that were previously impractical.
‘Based rollups’ take this concept further by outsourcing transaction sequencing directly to Ethereum’s validator set. This leverages L1-level decentralization while maintaining the scalability benefits of L2s – an elegant solution that sidesteps many trust assumptions altogether.
The upshot? Builders launching app-chains in 2025 can now choose between customizable decentralized sets (for tailored governance) or plug into shared networks for instant security bootstrapping. Both options dramatically improve fairness in transaction ordering and make it harder for bad actors to extract value at user expense.
Real-world adoption is accelerating as these models prove their worth. Starknet’s decentralization roadmap, for example, is focused on sequencer evolution and protocol governance, while other ecosystems are experimenting with rotating leader committees and Byzantine-fault-tolerant sequencing. The result: a new baseline for rollup security in 2025 that is more robust, transparent, and adaptable than anything seen in prior years.
Key Benefits of Decentralized Rollup Sequencers in 2025
-
Liveness: Decentralized sequencer networks like Cero ensure uninterrupted transaction processing, eliminating single points of failure and boosting network reliability.
-
Censorship Resistance: Platforms such as Astria use distributed sequencer sets to prevent any single entity from blocking or filtering transactions, safeguarding user rights and access.
-

Fair Transaction Ordering: Protocols implementing the Distributed Transaction Sequencing Strategy (DTSS) enforce transparent and equitable transaction ordering, reducing the risk of MEV extraction and unfair practices.
-
Shared Security: Based rollups leverage Ethereum’s mainnet validators as shared sequencers, inheriting Ethereum’s robust security and trustless guarantees for all participating rollups.
Critically, these advances address the persistent threat of MEV extraction. In centralized setups, sequencers could front-run or reorder trades for profit. Decentralized approaches like Distributed Transaction Sequencing Strategy (DTSS) enforce transparent ordering rules across multiple independent nodes, making it nearly impossible for any single participant to manipulate outcomes. This not only improves user trust but also attracts institutional capital wary of opaque or manipulable systems.
Shared sequencer networks are also reshaping the economics of app-chain deployment. By pooling security resources and compressing data across multiple rollups, they drive down costs while maintaining high throughput and rapid finality. For developers and enterprises evaluating their options in 2025, this means lower barriers to entry without compromising on core blockchain principles.
Looking Ahead: Building Trustless App-Chains
The move toward decentralized rollup sequencers isn’t just a technical upgrade – it’s a philosophical realignment with the original vision of blockchain: open participation, permissionless innovation, and credible neutrality. As roadmaps mature, expect to see even tighter integration between L1 validators and L2 sequencing logic, further blurring the lines between base layer security and application-specific customization.
For teams launching new app-chains or migrating legacy projects to modern infrastructure, the imperative is clear: prioritize censorship resistance and fair transaction ordering from day one. The ecosystem now offers composable building blocks – from hybrid committee models to fully shared sequencing layers – that make it possible to scale without sacrificing trustlessness.
The bottom line? 2025 marks a turning point where decentralized rollup sequencer designs are no longer experimental but essential for any project seeking longevity in an increasingly competitive landscape. Builders who adapt early will not only protect their users but also position themselves at the forefront of blockchain’s next era of scalable fairness.