In the evolving landscape of blockchain infrastructure, downtime is a dealbreaker. For appchain rollups in 2025, the stakes are higher than ever: users expect seamless uptime, and developers demand robust, censorship-resistant environments. The answer lies in decentralized sequencers, a critical innovation for ensuring network reliability and operational continuity.

Why Centralized Sequencers Fall Short
Historically, many rollup solutions have relied on centralized sequencers to order transactions and produce blocks. While this approach delivers speed and simplicity at launch, it introduces serious vulnerabilities. A single sequencer can become a single point of failure, risking downtime from technical outages or targeted attacks. Additionally, centralized control opens the door to transaction censorship and unfair MEV (Miner Extractable Value) extraction, threatening both user trust and economic fairness.
The industry has taken notice. As reported by blockchainsolutions. com. sa and reflected in recent QuickNode research, rollup sequencers are now recognized as pivotal to blockchain scalability, but only if they avoid centralization traps.
The Rise of Decentralized Sequencers: How They Work
Decentralized sequencers distribute transaction ordering across multiple independent nodes rather than relying on one entity. This structural shift brings several key advantages:
- Enhanced Fault Tolerance: If one node fails or is attacked, others continue processing blocks without interruption.
- Censorship Resistance: Rotating or committee-based models make it difficult for any single actor to suppress transactions.
- Fair MEV Distribution: Multiple participants share block production rewards transparently, aligning incentives across the ecosystem.
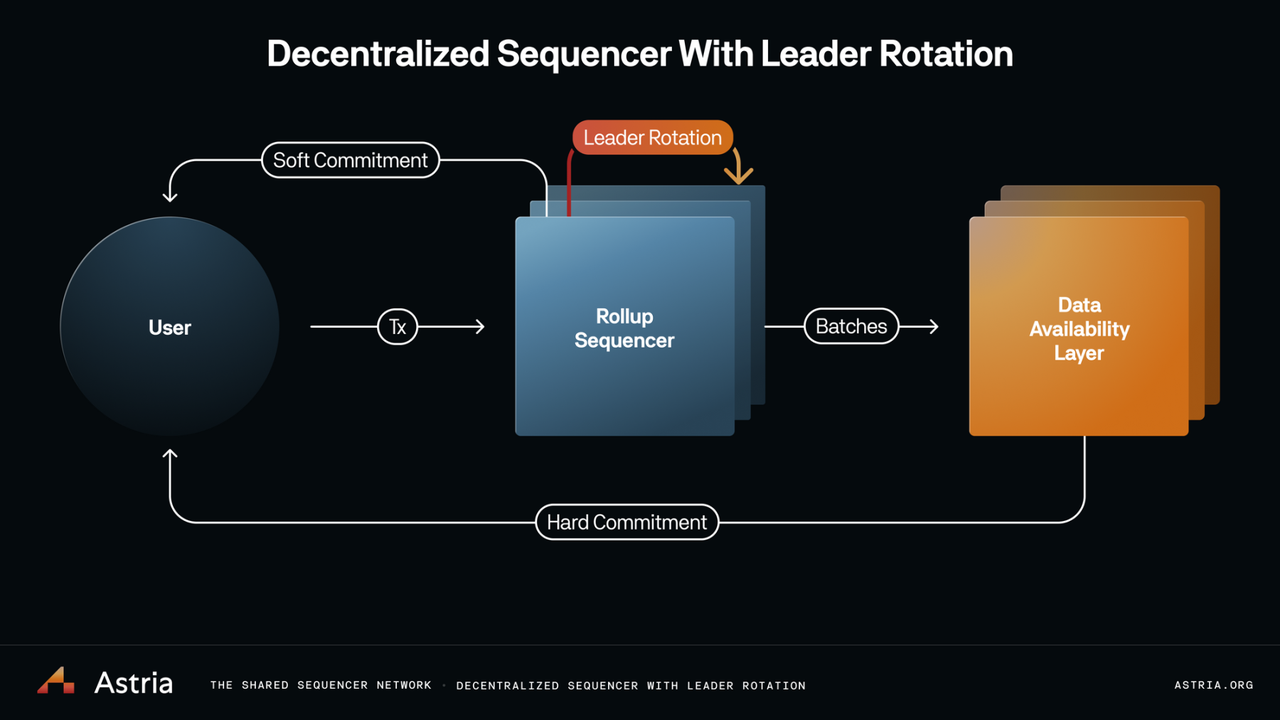
A standout example is Tanssi Network’s approach: sequencing duties rotate among a permissionless pool of staked nodes, with assignments managed by an orchestration chain. This ensures not only predictable performance but also dynamic adaptability as participants enter or exit the network.
Implementing Decentralized Sequencing in Your Appchain Rollup
If you’re building on OP Stack, Arbitrum Orbit, ZKsync Hyperchain, Polygon CDK, or leveraging top Rollup-As-A-Service providers, the blueprint for resilience starts with decentralizing your sequencing layer. Here’s what matters most:
- Rotating Assignments: Use randomized or stake-weighted rotation to assign sequencing duties among eligible nodes. This disrupts long-term collusion and supports open participation.
- On-Chain Monitoring and Enforcement: Integrate mechanisms that continuously track sequencer behavior, rewarding uptime and penalizing misbehavior automatically via smart contracts.
- External Finality Layers: Consider leveraging external validators or consensus layers for additional security backstops, separating transaction ordering from settlement enhances both reliability and trustlessness.
The latest research from Alchemy’s Dapp Store highlights shared sequencer networks like Espresso and Astria as emerging standards, allowing multiple rollups to benefit from collective security while maintaining their own sovereignty.
The Business Case: Uptime Is Non-Negotiable in 2025
The market context couldn’t be clearer: with user expectations at an all-time high and competition heating up among Layer 2 solutions, downtime translates directly into lost revenue and reputational damage. As Starknet’s decentralization roadmap shows, protocol governance is shifting toward community-driven models that prioritize continuous operation above all else. Rollup resilience isn’t just technical, it’s commercial survival.
To stay competitive in 2025, projects must treat appchain downtime prevention as a core business metric. The lessons from recent network disruptions are clear: even brief outages can erode user trust, trigger capital flight, and give rivals an opening. Decentralized sequencers are not just a technical upgrade, they’re a fundamental shift in how Web3 infrastructure is governed and monetized.
Top Benefits of Decentralized Sequencers for Appchain Rollups
-
1. Enhanced Fault Tolerance: Decentralized sequencers distribute transaction ordering across multiple nodes, ensuring continuous block production even if some nodes fail. For example, Tanssi Network assigns several sequencers per appchain, maintaining uptime and preventing single points of failure.
-

2. Censorship Resistance: By rotating sequencer roles and leveraging on-chain monitoring, decentralized sequencers minimize the risk of transaction censorship. Any attempt to censor can be detected and penalized, preserving network integrity and openness.
-
3. Fair MEV Distribution: Decentralized setups ensure that Miner Extractable Value (MEV) opportunities are shared among multiple participants. Tanssi’s transparent on-chain economics automatically distributes revenue, preventing MEV monopolization and fostering a fairer ecosystem.
-

4. Improved Security via External Finality Layers: Integrating external finality layers, as seen in modern rollup frameworks, adds an additional security backstop. This separation of ordering and settlement increases resistance to malicious activity and boosts trust in the rollup’s operation.
-
5. Greater Network Decentralization: Decentralized sequencers promote open participation by allowing new entrants to join the sequencer pool through staking or other consensus mechanisms. This broadens network control and reduces the risk of collusion or centralization.
-

6. Automated On-Chain Enforcement: With on-chain monitoring and enforcement, decentralized sequencer frameworks can automatically reward good performance and penalize downtime. This incentivizes reliability and ensures consistent service for appchain rollups.
The cost of ignoring decentralized sequencing is steep. Centralized models may offer initial ease but create hidden liabilities that compound over time: operational bottlenecks, opaque MEV extraction, and regulatory risks. In contrast, decentralized rollup deployment aligns incentives across operators, developers, and users, creating a more reliable foundation for growth and innovation.
Step-by-Step Guide: Deploying a Decentralized Sequencer Set
Projects leveraging Rollup-As-A-Service platforms can now access modular frameworks that make deploying decentralized sequencer sets straightforward. Whether you choose OP Stack for its EVM compatibility or ZKsync Hyperchain for privacy features, leading RaaS providers have streamlined the process:
- Account Creation and Framework Selection: Register with your chosen RaaS provider and select the framework that matches your technical requirements.
- Sequencer Pool Configuration: Define parameters for node participation, such as staking minimums or geographic distribution, to foster resilience.
- Monitoring and Governance Setup: Integrate on-chain monitoring tools and establish governance policies to handle misbehavior or upgrades.
- Mainnet Launch and Continuous Operation: Deploy your appchain with built-in rotation logic and external finality checks to maximize uptime from day one.
The industry’s direction is unmistakable. Shared sequencer networks like Espresso and Astria are gaining traction because they offer both security at scale and flexibility for bespoke deployments. As these solutions mature, expect more plug-and-play options, further reducing barriers to robust blockchain infrastructure reliability.
No single actor should ever be able to halt your network or capture all the value it generates. Decentralization isn’t just philosophy, it’s operational insurance.
The path forward is pragmatic: decentralize early, monitor continuously, and leverage the latest advancements in sequencing architecture. As protocols like Starknet push toward full community governance and as Rollup-As-A-Service providers standardize best practices, builders have never had more tools to ensure their networks stay live, even when conditions get volatile.
If you’re serious about rollup resilience in 2025, now is the time to architect your appchain around decentralized sequencers. It’s not just about technology, it’s about delivering on the promise of Web3: open access, continuous uptime, and fair value distribution for all participants.













